Today, integrating the best international practices into Ukraine’s tax system focuses on developing e-audit, which enhances transparency in working with financial reporting. Let’s delve into the details of implementing the Standard Audit File for Tax, or SAF-T – a file format developed by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) to standardize tax reporting and facilitate audits by tax authorities. The SAF-T format has already proven its effectiveness in many countries, including Portugal, France, Luxembourg, Austria, Germany, and others. SAF-T UA could become a powerful tool for Ukrainian businesses, reducing costs for both the state and companies while improving the efficiency of the State Tax Service (STS). Moreover, the SMART SAF-T UA solution will help companies face these upcoming changes with maximum readiness. How exactly? Let’s break it down below.
What Challenges Should Businesses Prepare For When Implementing the SAF-T UA Standard?
Bill No. 6255, “On Amendments to the Tax Code of Ukraine Regarding the Implementation of Electronic Audits (E-Audit)”, stipulates that starting from 2025, large taxpayers (LTPs) will be required to submit SAF-T UA reports annually. For other VAT payers, this reporting will become mandatory starting from 2027. The bill also provides for penalties for failing to submit SAF-T UA reports. Therefore, prudent entrepreneurs should prepare for these changes in advance to remain resilient to the following challenges:
- Technical Challenges: Ukrainian businesses may face difficulties integrating SAF-T UA with their existing ERP and CRM systems. Outdated software or the absence of necessary modules supporting SAF-T will complicate this process. Moreover, SAF-T requires a high level of data standardization and accuracy. Businesses must ensure that all financial information submitted to tax authorities is accurate, structured, and compliant with SAF-T format requirements. Implementing SAF-T demands modernization of accounting systems and automation of data collection, verification, and processing. This process may require additional resources to adapt or implement new solutions.
- Organizational Challenges: Businesses will need to prepare their staff for the specifics of submitting reports in the SAF-T UA format. Companies will have to review and improve their internal accounting and reporting processes. This will require significant effort to optimize and adapt processes to meet new requirements. However, having a specialized technical solution can facilitate a faster adaptation for businesses. Automating the exchange of information between businesses and tax authorities will reduce the time spent processing large data volumes, minimize error risks, and lessen the burden on accounting and financial departments.
- Financial Challenges: Implementing and adapting systems to support SAF-T UA will require additional financial investments. These may include costs for software licensing, hiring consultants, and upgrading technical equipment. Companies may also need additional IT support to ensure systems function properly and to prevent potential technical issues.
- Legal and Regulatory Challenges: SAF-T UA entails strict compliance with reporting standards, the State Tax Service’s data processing system restrictions, and regulatory requirements that may change over time. For instance, the STS-developed SAF-T UA file was introduced in 2022 and has already undergone four updates. Businesses will need to closely monitor legislative changes to comply with current requirements. Additionally, since SAF-T UA involves transferring large volumes of sensitive information to tax authorities electronically, companies must ensure data security and protection against cyber threats.
- Challenges in Control and Auditing: Tax audits will become more automated, reducing the influence of the “human factor.” However, companies must be ready for increased accountability for the accuracy of their data and reports, as errors could quickly result in fines or additional audits.
Features of the SAF-T UA File Structure and the Importance of Automating Reporting Processes
The most frequently asked questions from businesses regarding the new electronic reporting standard revolve around data collection, processing, and the structure of the SAF-T UA file. Each component of this structure has strict requirements and demands a meticulous approach to ensure compliance:
- Header – The header is a mandatory element for correctly exporting the file. It contains general information about the SAF-T UA file, details about the business entity, and information about the reporting period.
- MasterFiles – These are used to provide information referenced in other sections. They include accounting policies, master data of counterparties, inventories, and turnover records. These files ensure data structure and accuracy. When submitting a file for a specific period, it is essential to export only the master data used in accounting entries. For example, when exporting a client’s balance sheet, it is necessary to obtain a turnover report that shows the opening balance, transactions during the period, and the closing balance. The client master data should include only those counterparties with whom transactions occurred or who have a balance during the reporting period.
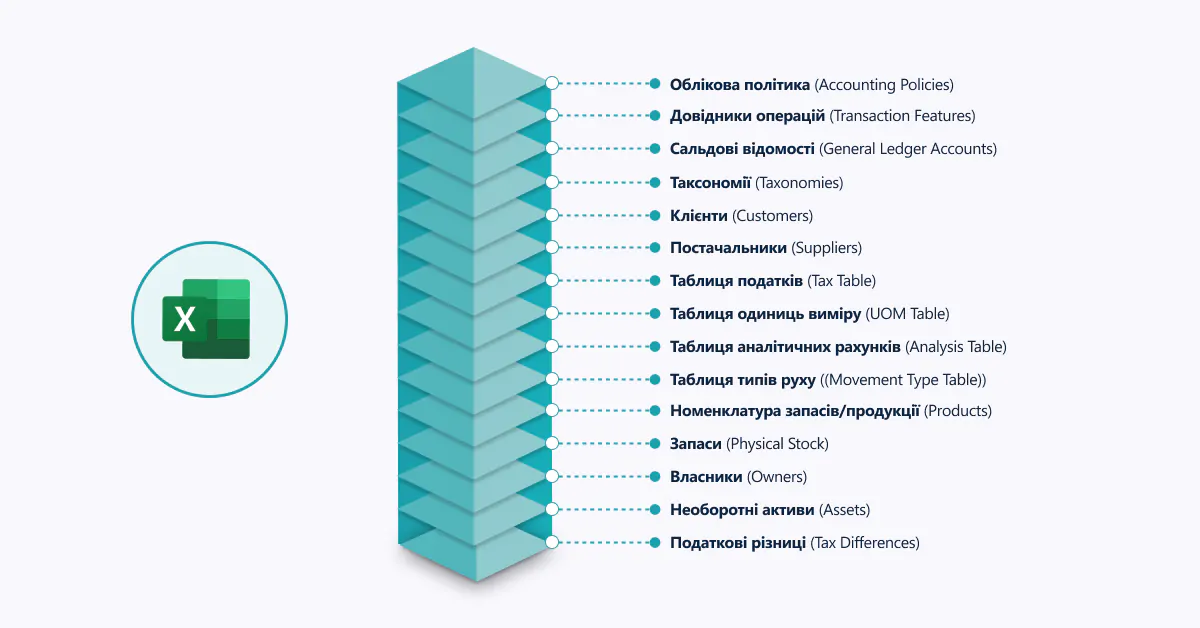
There are 15 types of master files in SAF-T UA, each with its own requirements for completion. For instance, some master files may have only 2–3 mandatory fields, while others may require up to 10. Therefore, it is essential that any automation solution includes system-level checks, as non-compliant data may lead to the file being rejected by the tax authorities. The system should ensure automated control over field completion, significantly simplifying the reporting preparation process.
- GeneralLedgerEntries – This section of the SAF-T file provides information on accounting operations and transactions for the selected period.
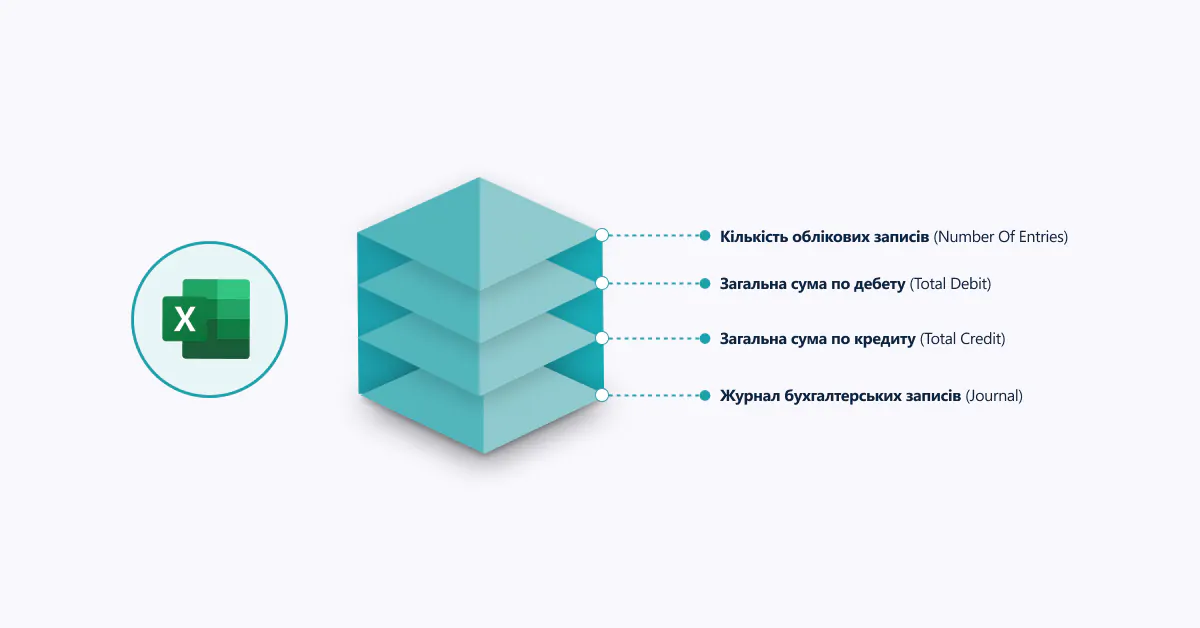
When generating this section, it is important to consider document identification, as each transaction and document must reference specific identifiers, such as buyers, suppliers, or addresses. This ensures that only related and accurate data is included. Automation can significantly simplify an accountant’s work since specialized systems can extract data from accounts and documents automatically, avoiding manual input and minimizing human error. The solution should validate the data and verify identifier compliance, ensuring that all transactions and documents have correct references. An automated approach simplifies reporting and enhances data accuracy in the SAF-T UA file, allowing companies to be confident in the correctness of their financial reports and reducing the risk of issues during tax audits.
- SourceDocuments – This section is designed to provide information on all primary documents. It is important to export only the specified document types for the reporting period, focusing on the most critical information. The submission procedure for such documents must be strictly regulated, as improper submission may lead to negative consequences for the company. Companies should consider solutions that simplify this process through automation. The system should automatically identify the required documents and ensure their proper processing. This functionality helps businesses meet tax requirements with minimal time and resource investment.
Thus, the proper organization of data structures and their interconnections is critical for efficient work with SAF-T UA files. SMART business has thoroughly examined all aspects of this task and incorporated them into its SMART SAF-T UA solution, which simplifies reporting processes through automation and minimizes the risk of errors.
Request a demo
Functional Advantages of SMART SAF-T UA and Answers to Common Questions for Those Seeking the Optimal Solution

When developing SMART SAF-T UA, SMART business thoroughly studied and monitored current changes in this area to meet all the requirements specified by the State Tax Service (STS) in each of its releases. The developer considered the regulatory framework that underpins SAF-T UA development:
- Law of Ukraine “On Electronic Documents and Electronic Document Management”,
- Orders of the Ministry of Finance:
- Order No. 561 – amendments regarding electronic audit (E-audit) to Order No. 1393.
- Order No. 1393 – “On Approving the Procedure for Providing Documents in Electronic Form by Large Taxpayers”.
- The Tax Code of Ukraine, which regulates aspects of tax reporting and electronic document management.
- OECD Guidance, including the SAF-T file guidelines and the schema to ensure compliance with international standards for electronic accounting.
- Order No. 729 of the Ministry of Revenues and Duties – “On Approving the Format (Standard) of the Reporting Entity’s Electronic Document.”
- The Concept of E-Audit Implementation for Taxpayers, issued by the Ministry of Finance.
These and other regulations form the legal, technical, and methodological basis for implementing SMART SAF-T UA, ensuring compliance with both local and international standards for electronic audit and document management. As a result, SMART SAF-T UA was introduced to the Ukrainian market as an additional integration that enhances the functionality of Business Central and SMART Accounting for Ukraine. The solution offers the following capabilities:
- Generating SAF-T Files in XML Format – SMART SAF-T UA automatically creates XML-based reporting files according to the standards approved by the STS of Ukraine. The data in the SAF-T file is strictly organized following the XSD schema, specifying the required elements, attributes, and their hierarchy. This includes detailed information on transactions, accounts, VAT invoices, and more. With a solution from SMART business, the SAF-T file format and structure fully meet the technical requirements of tax authorities, enabling seamless uploads to the STS portals via the Taxpayer’s Electronic Cabinet.
- Report Generation Using Business Central Accounting Data – The solution integrates with Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central, allowing automated reporting based on existing system data. This means essential financial, tax, and accounting information – such as accounts, transactions, VAT invoices, and payroll – are automatically extracted. Users don’t need to manually transfer or verify data, as the system automates these processes, minimizing manual effort and reducing the likelihood of human errors.
- Data Validation for SAF-T Technical Requirements – The solution includes built-in functionality to automatically validate data before generating the SAF-T file. For instance, it checks whether all mandatory fields are filled, whether formatting requirements are met (e.g., correct date formats, identifiers, tax numbers, etc.). If discrepancies are found, the system identifies problematic areas (e.g., missing required fields or incorrect data formats) and allows users to make corrections quickly. The data is checked before the SAF-T file is generated, preventing the submission of reports with errors. Thus, thanks to the built-in validation, there is no need to correct errors after the file is uploaded to the tax service, which is usually a more complex and lengthy process. The solution ensures that all data elements and attributes comply with the standards defined in the SAF-T element description (XSD schema).
- Data Preview Table Generation – The solution provides options to generate tables for data preview before the information is finalized in the SAF-T file or uploaded to the tax system. This feature is especially useful for handling large datasets, where manually reviewing XML reports would be challenging. Detected errors or discrepancies can be corrected conveniently. Additionally, preview tables can be exported to Excel for further adjustments and re-imported into the system as needed.
- Saving Draft Reports in the System – During report creation and submission, users can save incomplete or draft versions of their reports. These drafts are stored in the system, allowing users to revisit them later for review, adjustments, or finalization. This feature simplifies report editing by enabling a step-by-step and flexible approach to document preparation.
- Selective Table Export Upon Tax Authority Requests – Since tax authorities may request specific data depending on the situation, selective data export enables users to provide only the required information at a given moment. For such specific inquiries, users can quickly access the needed data without manually searching or consolidating information from different systems. This functionality allows accounting departments to respond swiftly and effectively to tax authority requests, always ensuring readiness for audits.
- Generating ZIP Archives for XML Files – SMART SAF-T UA automatically packages XML-based reporting files into ZIP archives. The system ensures files are stored and transmitted in the format required by tax authorities, meeting the requirements for submitting documents via the Taxpayer’s Electronic Cabinet. This feature saves time and resources for your specialists while ensuring files are correctly packaged and ready for upload.
In conclusion, continuous compliance with STS requirements, regular system updates, an intuitive interface, automated file generation in the correct format, and integration with other Microsoft products provide a unified platform for managing your company’s core business processes efficiently.
Still have questions about automating SAF-T UA report generation with SMART business solutions? Check out answers to frequently asked questions from financial directors, chief accountants, IT specialists, department managers, and other professionals preparing for upcoming changes. Or request a system demo and see all the benefits of implementing SMART SAF-T UA for yourself:


